PURA Legislative Mandate
PURA was initially created by The Gambia Public Utilities Regulatory Authority Act, 2001 (the “PURA Act”) as an independent agency with the mandate to regulate certain “regulated public services”, which are defined in section 2(1) of the act as meaning “a communication service, a transport service, an energy service or a water service provided directly or indirectly to the public or to any section of the public”.
PURA plays a pivotal role among policy makers, including the Office of the President, Ministry of Information and Communication Infrastructure (MOICI) and Ministry of Energy, and licensed service providers and consumers. The President of The Gambia appoints the members of the Board of PURA including the Director General.
PURA Functions
To facilitate PURA’s regulation of public utilities, section 13(1) of The Gambia Public Utilities Regulatory Authority Act, 2001 (among other things) mandates PURA to provide guidelines on and examine rates and fees for the provision of regulated public services; protect the interest of consumers and of public utilities; monitor and enforce standards of performance by public utilities; and promote fair competition among public utilities.
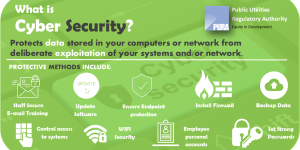
In addition to the PURA Act, the functions and role of PURA are further defined in the Information and Communications Act, 2009 (the IC Act) and the Electricity Act 2005. The IC Act 2009 sets out PURA’s mandate as the authority responsible for the regulation of information and communications services, information and communications networks, associated facilities and associated services. The IC Act 2009 assigns additional functions to PURA and clarifies functions granted to PURA under the PURA Act. The Electricity Act 2005 similarly assigns additional functions to PURA and clarifies functions granted to PURA under the PURA Act.
PURA Organizational Structure
While the PURA Act establishes the membership of the board of PURA, the Authority’s management has a flexible organizational structure which is currently composed of the following departments. The Director General is supported by Directors of seven departments:
- Finance and Administration
- Human Resources and Corporate Affairs
- Economic Regulation
- Information & Communications Technology
- Energy – including Electricity and Water
- Consumer Affairs
- Legal, Licensing and Enforcement